WordPress.com AI Assistant overview: deeper AI integration for building and editing sites
WordPress.com has launched an AI Assistant positioned as part of a broader wave of AI-powered website builders—but with a focus that goes beyond just generating website copy. The core idea is simple: the assistant can understand a site’s content and layout, so you can request more complex changes using natural language prompts.
Instead of relying on manual tweaks, copying/pasting content, or figuring out how to phrase “perfect prompts,” the AI Assistant is designed to translate everyday requests into real changes across your WordPress.com site—without requiring code.
Natural language prompts that change layout, styles, and page structure
Website layout edits without code or “prompt engineering”
A key capability is making site layout changes through natural language prompts. WordPress.com frames this as reducing friction: no copy-pasting, no prompt engineering, and no code needed to understand what to do next.
What the AI Assistant can adjust inside the editor
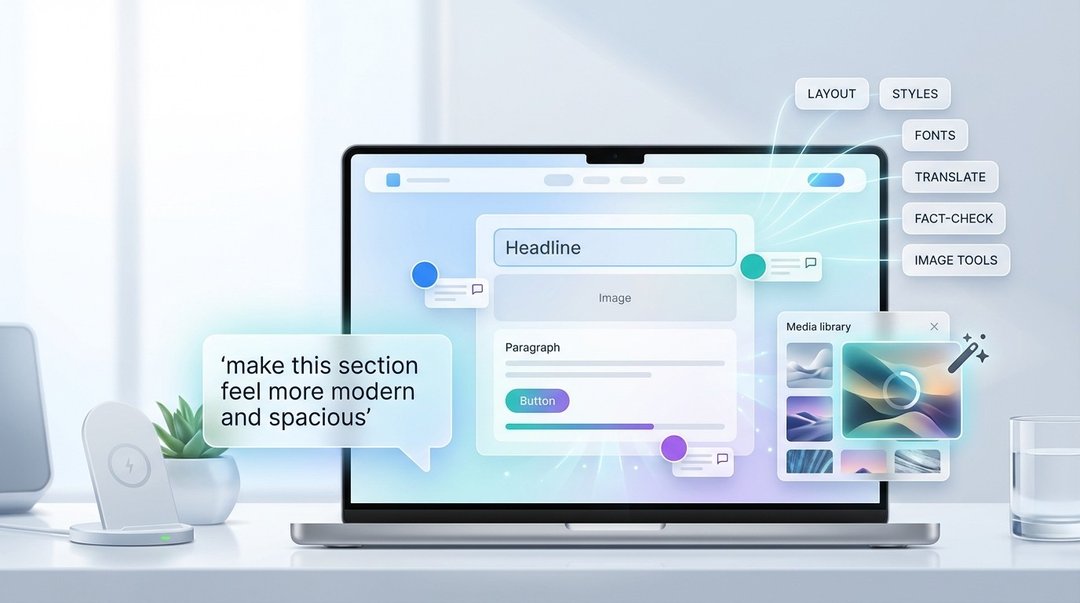
The AI Assistant supports a range of design and structure changes, including:
- Layout adjustments
- Style updates
- Color changes
- Font tweaks
- Page structure edits
WordPress.com also demonstrates that the assistant can work from broad direction, not just highly detailed instructions. One example prompt shown is: “Make this section feel more modern and spacious.” The takeaway is that the AI Assistant is meant to handle subjective, vibe-based requests and translate them into tangible visual updates.
Context-aware writing and editing: generate, refine, and translate website content
Content creation and editing with context
WordPress.com highlights “creating and editing content with context” as one of the three main areas where the AI Assistant helps. In practice, that positioning suggests the assistant isn’t only producing generic text—it’s designed to take into account what’s already on the site when generating or editing content.
Copy-related tasks: generate and translate text
Beyond design changes, the assistant covers copy workflows like:
- Generating text
- Translating text
So it’s not just a design helper—it’s also presented as an AI writing and editing layer inside WordPress.com.
AI image generation and editing inside WordPress.com media library
Built-in image creation using Google Nano Banana models
WordPress.com integrates image generation and editing directly into the media library, powered by Google’s Nano Banana models. The practical benefit is workflow simplicity: users can generate and edit images without jumping out to third-party platforms.
Faster creative iteration without external tools
Because it’s embedded where your site assets already live (the media library), the AI Assistant’s image features are positioned as a more direct path from idea → asset → publish, especially for site owners who want visual updates without extra tools.
Colleague-style collaboration: block notes editor and AI-assisted feedback
Block notes editor for shared comments and collaboration
WordPress.com points to “colleague-style collaboration” as the third key area. This includes a block notes editor, introduced with WordPress 6.9, which gives collaborators a dedicated space to share comments and work together.
AI in collaboration: fact-checking and edit suggestions
Inside this collaborative layer, the AI Assistant can contribute by:
- Fact-checking
- Making edit suggestions
So the assistant isn’t only a solo creator tool—it’s also framed as something that supports review cycles and on-page feedback in a shared workspace.
How to enable WordPress AI Assistant: availability and opt-in settings
Generally available, but requires opt-in
WordPress AI Assistant is described as generally available, but it isn’t automatically active for everyone. Users need to enable it manually via:
Sites > Settings > AI tools
Enabled by default for AI website builder sites
There’s one exception: sites that were already built using the AI website builder option will have the AI Assistant enabled by default.